LOTUCE: a new instrument for dome turbulence characterization
Within the framework of site qualification for the E-ELT and its dome design, local turbulence due to the immediate environment of the telescope must be taken into account. A better knowledge of the phenomenon and its modeling becomes crucial if one wants to optimize the performances of the telescope. However, in contrast with the rest of the atmosphere, the surface layer turbulence is affected by ground and environment characteristics (convective flow, roughness, etc.). Some models were proposed to link the image quality to the heat dissipation in the surface layer. A new instrument was developed by our group for the characterization of the local turbulence inside the telescope enclosure. It consists of the wavefront analysis by means of parallel laser beams on a multi-baseline configuration. The fluctuations of the angle of arrival (AA) are measured with CCD camera and their longitudinal and transverse covariances at different baselines are compared to the theoretical ones. The choice of the configuration of the parallel beams is important to obtain an optimal sampling of these AA covariances. Other statistics of these measured AA fluctuations lead also the local Fried parameter, outer scale and coherence time.
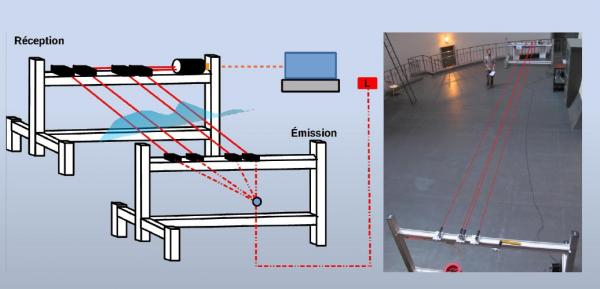
Principle of the Lotuce instrument.
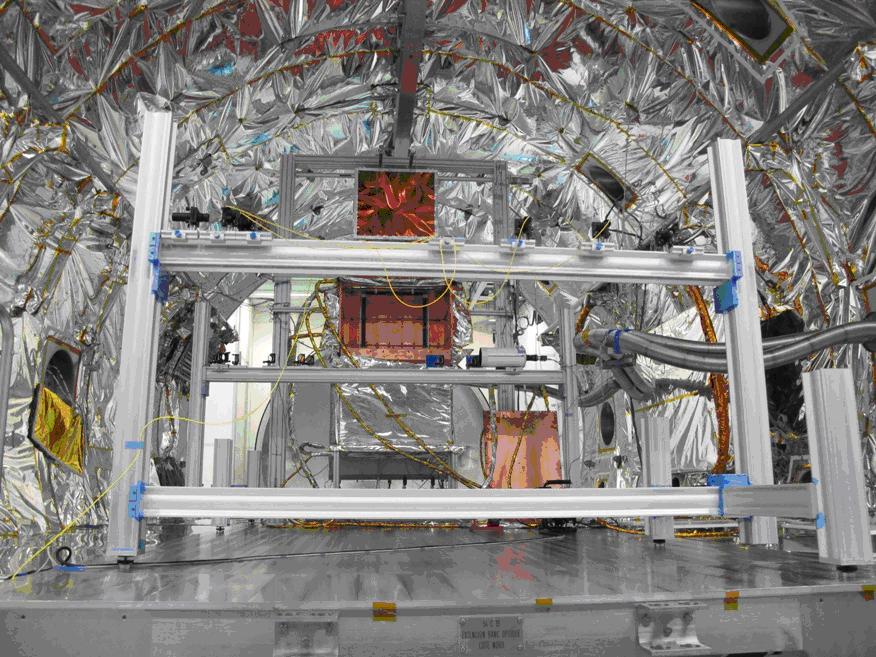
INTENSE: a new instrument for turbulence charcterization inside clean rooms of spatial laboratories
(Fried parameter, structure function CN2 and outer scale). The temporal spectrum of A.A fluctuation can be compared to existing models and cut-o- frequencies can be extracted to calculate the wind speed and the size of the outer scale. Moreover the -ve parallel laser beams leading to ten di-fferent baselines from 0.05 to 2.5m
in addition to the variance measurement are used to -fit with the theoretical models. Our instrument has been constructed in order to work in a noisy industrial environment where multiple vibrations sources can interfere with the A.A fluctuation measurements. During several measurement campaigns, we have found various turbulence conditions depending on clean room rating and air regulation condition. Our results give new insight into clean room design for optical instrument testing and integration.